Achieving peak physical performance, whether in the gym, on the field, or simply in daily life, hinges significantly on what you consume. For those aiming for sustained energy throughout the day and consistent muscle growth, the question of optimal fuel is paramount. It’s not just about eating enough; it’s about eating smart, understanding how different nutrients contribute to your body’s intricate processes.
Understanding the Pillars of Nutrition: Macronutrients
The foundation of any diet for energy and muscle gain lies in macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each plays a distinct yet interconnected role in fueling your body, repairing tissues, and supporting vital functions. Getting the right balance tailored to your activity level and goals is crucial.

Carbohydrates: The Primary Energy Source
Often misunderstood, carbohydrates are your body’s preferred and most efficient source of energy. They are broken down into glucose, which is used immediately for fuel or stored as glycogen in the liver and muscles for later use. For sustained energy, focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, which release glucose slowly, preventing energy crashes. Simple sugars, while providing quick energy, should be consumed sparingly, primarily post-workout if needed.
Adequate carbohydrate intake is also vital for preventing muscle breakdown, as your body will turn to protein for energy if carb stores are depleted, thereby hindering muscle gain.
Proteins: The Building Blocks of Muscle
Protein is indispensable for muscle synthesis and repair. During exercise, muscle fibers experience micro-tears, and protein provides the amino acids necessary to rebuild and strengthen them, leading to muscle growth (hypertrophy). Beyond muscle, protein also supports enzyme production, hormone regulation, and immune function. Sources include lean meats, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy, legumes, and plant-based protein powders.

Fats: Long-Lasting Energy and Hormonal Support
Dietary fats are crucial for long-term energy, especially during lower-intensity or prolonged activities. They also play a critical role in hormone production, nutrient absorption (fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, K), and insulating organs. Healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are beneficial. Saturated fats should be consumed in moderation, while trans fats should be avoided.

The Synergy of Macronutrients: Finding Your Balance
The optimal approach isn’t to demonize or overemphasize one macronutrient. Instead, it’s about creating a synergistic balance. A plate rich in complex carbohydrates, lean protein, and healthy fats ensures a steady supply of energy, supports muscle recovery, and provides the necessary nutrients for overall health. For example, a meal combining brown rice (complex carb), chicken breast (protein), and avocado (healthy fat) offers a complete nutritional profile.
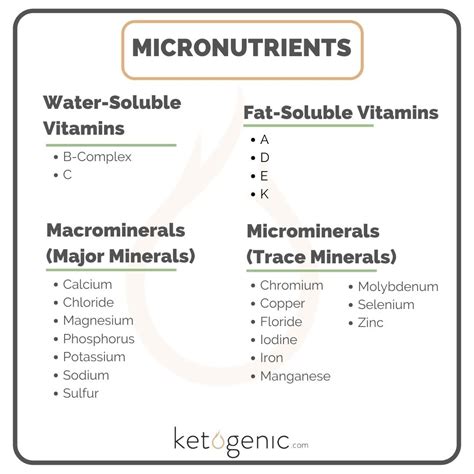
Beyond Macros: Micronutrients and Hydration
While macronutrients provide the bulk of energy and building blocks, micronutrients (vitamins and minerals) are the catalysts for countless bodily functions, including energy production, muscle contraction, and immune support. A diet rich in diverse fruits, vegetables, and whole foods ensures adequate micronutrient intake. Similarly, hydration is non-negotiable. Water transports nutrients, regulates body temperature, lubricates joints, and plays a role in nearly every metabolic process, directly impacting energy levels and performance.
Timing and Individualization
When you eat can be almost as important as what you eat, especially around workouts. Consuming carbohydrates and protein before and after training can optimize performance and recovery. However, the exact ratios and timing can vary significantly based on individual goals, body type, activity level, and dietary preferences. Consulting with a sports nutritionist or dietitian can help tailor a plan specifically for you.

Conclusion
The optimal fuel for sustained energy and muscle gain isn’t a single food or a magic pill; it’s a holistic approach to nutrition. It involves a strategic intake of complex carbohydrates for energy, sufficient protein for muscle repair and growth, and healthy fats for long-term fuel and hormonal balance. Supplement this with abundant micronutrients and consistent hydration, and you’ll lay a robust foundation for achieving your physical peak and maintaining a vibrant, energetic lifestyle. Prioritize whole, unprocessed foods, listen to your body, and adjust your intake as your needs evolve.