Understanding Time Efficiency in Workouts
For many men, the quest to build muscle and burn fat is often met with the challenge of limited time. A demanding career, family responsibilities, and other commitments can make it difficult to dedicate hours to the gym each week. The good news is that you don’t need endless hours; you need an intelligent, time-efficient workout split. The goal is to maximize muscle protein synthesis and energy expenditure within a condensed timeframe, promoting both hypertrophy and fat loss.
The key to efficiency lies in selecting a split that allows for sufficient frequency and volume for each muscle group without excessive overlap or wasted time. This means hitting muscles hard enough to stimulate growth, providing adequate recovery, and burning enough calories to contribute to a deficit.

Common Workout Splits: A Quick Review
Before diving into the most efficient option, let’s briefly look at some popular workout splits and their general characteristics:
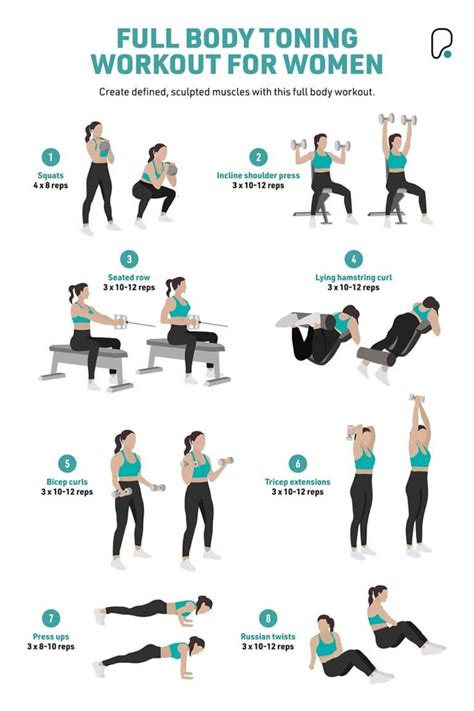
Full Body Workout
- Description: Every major muscle group is trained in a single session.
- Frequency: Typically 2-4 times per week.
- Pros: High frequency for each muscle group, excellent for beginners, high caloric burn per session.
- Cons: Can be very taxing if volume per muscle group is too high, may require shorter sessions.
Upper/Lower Split
- Description: Upper body trained on one day, lower body (including core) on another.
- Frequency: Typically 4 times per week (2 upper, 2 lower).
- Pros: Allows for more volume per muscle group than full body, good recovery between sessions.
- Cons: Requires 4 dedicated gym days, which might be too much for some schedules.
Push/Pull/Legs (PPL) Split
- Description: Pushing movements (chest, shoulders, triceps), pulling movements (back, biceps), and leg movements (quads, hamstrings, calves) are separated.
- Frequency: Often 3 or 6 times per week.
- Pros: Excellent for volume and targeting specific muscle groups, good for intermediate to advanced lifters.
- Cons: A 6-day split is very time-consuming; a 3-day split means lower frequency per muscle group.
The Champion for Time-Efficiency: Full Body or Upper/Lower
When it comes to building muscle and burning fat in a time-efficient manner, the Full Body workout split and the Upper/Lower split often emerge as the top contenders, largely due to their optimal frequency and flexibility.
Why Full Body Workouts Excel
For men with only 2-3 days a week to train, a Full Body split is arguably the most time-efficient. You hit every major muscle group multiple times per week, which is crucial for muscle protein synthesis and metabolic boost. Each session focuses on compound movements, engaging multiple muscles simultaneously, which translates to a higher caloric expenditure per workout – perfect for fat loss. A typical structure might be:
- Day 1: Full Body A
- Day 2: Rest/Active Recovery
- Day 3: Full Body B
- Day 4: Rest/Active Recovery
- Day 5: Full Body C
- Day 6-7: Rest/Active Recovery
Each workout can be intense but shorter (45-60 minutes) due to fewer exercises per muscle group, allowing you to get in, get it done, and get out. The high frequency keeps your metabolism elevated throughout the week.

The Upper/Lower Split Advantage for Slightly More Time
If you have 4 days a week to dedicate, an Upper/Lower split becomes incredibly efficient. It allows for higher volume per muscle group per session compared to a full-body workout, potentially leading to more hypertrophy. The 2x per week frequency for each muscle group is still excellent for muscle growth and fat burning. A common setup:
- Day 1: Upper Body
- Day 2: Lower Body
- Day 3: Rest
- Day 4: Upper Body
- Day 5: Lower Body
- Day 6-7: Rest/Active Recovery
This split allows for deeper fatigue in muscle groups while still providing adequate rest for recovery, optimizing both growth and performance.
Optimizing Your Chosen Split for Maximum Results
Regardless of whether you choose Full Body or Upper/Lower, these strategies will enhance your time efficiency and results:
Prioritize Compound Movements
Exercises like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, overhead presses, and rows work multiple muscle groups simultaneously, giving you the biggest bang for your buck in terms of muscle activation and caloric burn. Focus on 2-4 compound exercises per workout.
Implement Progressive Overload
To ensure continuous muscle growth, you must progressively challenge your muscles. This means gradually increasing the weight, reps, sets, or decreasing rest times over time. Tracking your progress is essential.

Use Supersets or Drop Sets (Judiciously)
To save time, pair non-competing exercises (e.g., bench press followed by rows) as supersets, or incorporate drop sets at the end of an exercise to maximize muscle fatigue in less time. Be mindful not to overdo it, as this can lead to burnout.
Maintain Intensity and Focus
When time is limited, every minute counts. Minimize distractions, keep rest periods between sets concise (60-90 seconds for compound, 30-60 for isolation), and maintain a high level of effort throughout your workout.
Don’t Neglect Nutrition and Recovery
No matter how efficient your workout split, your diet and recovery are paramount for muscle growth and fat loss. Ensure adequate protein intake, a slight caloric deficit for fat loss, and sufficient sleep to allow your body to repair and rebuild.

Conclusion
For men aiming to build muscle and burn fat efficiently, a Full Body split (2-3 times/week) or an Upper/Lower split (4 times/week) offers the best balance of frequency, volume, and recovery. Both allow for intense, productive sessions that maximize your time in the gym. Combine your chosen split with compound movements, progressive overload, and intelligent intensity techniques, and you’ll be well on your way to achieving your physique goals without sacrificing your entire schedule.




