The Vital Link Between Hydration and Cellular Power
For a man seeking optimal performance, both physically and mentally, the concept of energy is paramount. This energy isn’t just about what’s derived from food; it fundamentally originates at the cellular level, primarily through the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). While diet and exercise often take center stage in discussions about energy, the role of consistent hydration is frequently underestimated, yet profoundly impactful. Water, making up a significant portion of the human body, is not merely a thirst quencher but an essential solvent and participant in nearly every biochemical reaction that fuels our cells.
Understanding how water directly influences the intricate machinery within our cells is key to appreciating its importance. From transporting vital nutrients to facilitating enzymatic reactions, water is the medium through which life-sustaining processes occur. Without adequate hydration, these processes falter, leading to a noticeable decline in cellular efficiency and, consequently, overall energy levels.

Water: The Unsung Hero of Metabolism
Every cell in a man’s body relies on water to function correctly. It acts as a universal solvent, dissolving minerals, vitamins, amino acids, glucose, and other substances, making them accessible for metabolic use. Water transports these essential nutrients to cells and carries away waste products, such as urea and carbon dioxide, ensuring a clean and efficient cellular environment. This continuous exchange is critical for maintaining homeostasis and enabling cells to perform their energy-generating tasks without interference from accumulating toxins.
Beyond transportation, water is a direct reactant in many metabolic pathways. Hydrolysis, for instance, a chemical reaction involving water, is fundamental to breaking down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats into smaller molecules that can be used for energy or building blocks. Without sufficient water, these catabolic processes slow down, impeding the initial steps of energy extraction from food sources.
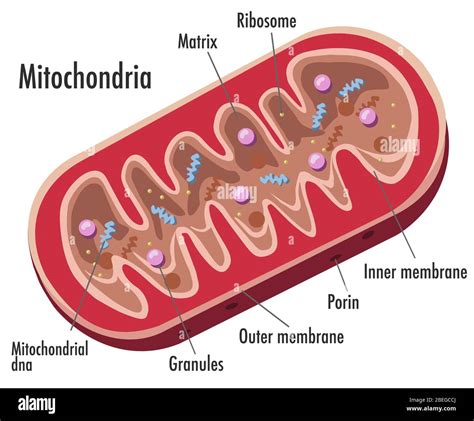
Mitochondria: The Cell’s Powerhouses Need Water
The mitochondria, often dubbed the ‘powerhouses’ of the cell, are where the bulk of ATP is generated through cellular respiration. This complex series of reactions, including the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation, requires an aqueous environment to proceed efficiently. Water plays a role in maintaining the structural integrity of mitochondrial membranes and ensures the proper flow of electrons, which is central to ATP synthesis.
When a man is consistently under-hydrated, even subtly, the cellular fluid balance is disrupted. This can lead to a less optimal environment within the mitochondria, making enzymatic reactions less efficient. The result is a reduction in the rate and quantity of ATP produced. Imagine a well-oiled machine suddenly running on insufficient lubricant; it will still operate, but far less efficiently, leading to wear and tear and decreased output.
The Cost of Dehydration: Sluggish Cells, Lagging Energy
Even mild dehydration (a 1-2% drop in body water content) can significantly impair physical and cognitive function in men. This impairment directly correlates with reduced cellular energy efficiency. Symptoms like fatigue, lethargy, decreased concentration, and muscle weakness are direct manifestations of cells struggling to produce enough ATP to meet demand. Nerve impulses slow down, muscle contractions become less powerful, and cognitive processing becomes sluggish because the cells responsible for these functions lack adequate energy fuel.
Furthermore, dehydration thickens the blood, making the cardiovascular system work harder to pump oxygen and nutrients to cells, further taxing the body’s energy reserves. This cascade of events underscores how central water is to maintaining the high energy demands of a man’s active physiology.

Beyond Thirst: The Role of Electrolytes
While water intake is crucial, the balance of electrolytes (like sodium, potassium, and magnesium) is equally vital for maintaining proper fluid balance both inside and outside cells. Electrolytes facilitate osmosis, the movement of water across cell membranes, ensuring that cells are adequately hydrated and can effectively exchange substances. An imbalance in electrolytes, often exacerbated by insufficient water intake, can impair cellular function and, by extension, energy production.
Many men, especially those who are physically active, lose electrolytes through sweat. Replenishing both water and these crucial minerals is essential to support the efficient cellular processes that underpin energy generation. This isn’t just about drinking plain water; it’s about smart hydration that supports the entire cellular environment.
Strategies for Optimal Hydration and Sustained Energy
To ensure consistent hydration and maximize cellular energy production, men should aim for proactive rather than reactive drinking. Don’t wait until you’re thirsty; by then, you’re already in a state of mild dehydration. Key strategies include:
- Start Early: Drink a glass of water first thing in the morning to rehydrate after sleep.
- Carry Water: Keep a water bottle handy throughout the day to encourage regular sips.
- Set Reminders: Use apps or alarms to remind yourself to drink water at regular intervals.
- Incorporate Hydrating Foods: Fruits and vegetables like watermelon, cucumber, oranges, and spinach have high water content.
- Adjust for Activity: Increase water intake significantly during exercise, hot weather, or when experiencing illness. Consider electrolyte-enhanced beverages for prolonged strenuous activity.
- Monitor Urine Color: Pale yellow urine is generally a good indicator of adequate hydration.

Conclusion: Fueling Your Cells for Peak Performance
Consistent hydration is far more than just staying quenched; it is a fundamental pillar of cellular health and, consequently, optimal energy production in men. By providing the essential medium for metabolic reactions, nutrient transport, waste removal, and mitochondrial efficiency, water directly influences how effectively your body generates ATP. Prioritizing smart, consistent hydration practices isn’t just about feeling better; it’s about empowering every cell in your body to perform at its peak, leading to sustained energy, improved cognitive function, and enhanced overall well-being. Make water your primary fuel, and experience the profound impact it has on your vitality.