Achieving a physique that is both muscular and lean is a common goal for many men. While dedication in the gym is crucial, the effectiveness of your efforts largely hinges on your workout split – how you divide your training days and target different muscle groups. An optimized split can dramatically accelerate both muscle gain and fat loss, creating a synergistic effect that traditional, less structured approaches often miss.
Understanding the Core Principles of Muscle Gain and Fat Loss
To optimize your split, you first need to understand the underlying principles. For muscle gain (hypertrophy), key factors include progressive overload (consistently increasing resistance, reps, or volume), sufficient training volume and intensity, and adequate protein intake. For fat loss, creating a caloric deficit is paramount, often combined with cardio and resistance training to preserve muscle mass.
An effective workout split for men will ensure each muscle group is trained with sufficient frequency (typically 2-3 times per week for optimal growth), allowing for adequate recovery between sessions. Volume should be high enough to stimulate growth but not so excessive that it impairs recovery. Prioritizing compound movements like squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and rows will engage more muscle fibers, burn more calories, and elicit a greater anabolic response.

Popular Workout Splits for Optimal Results
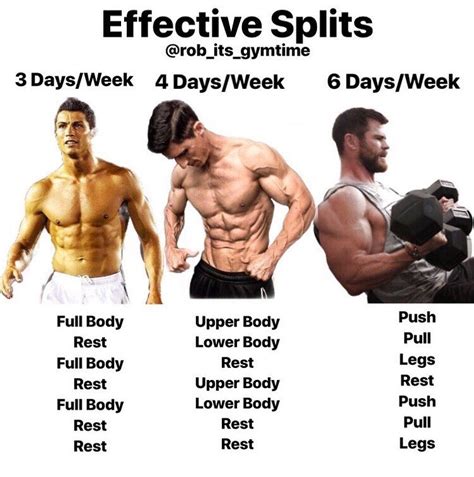
Several workout splits are highly effective for men aiming for muscle gain and fat loss. The best choice depends on your experience level, time commitment, and recovery capacity:
- Push/Pull/Legs (PPL): This split involves three distinct workouts: push (chest, shoulders, triceps), pull (back, biceps), and legs (quads, hamstrings, glutes, calves). It can be run 2-3 times a week (e.g., PPLRPPLR, where R is rest), allowing high frequency for each muscle group. It’s excellent for intermediate to advanced lifters due to its volume and frequency.
- Upper/Lower: A straightforward split dividing the body into upper body and lower body workouts. Typically done 4 days a week (e.g., Upper, Lower, Rest, Upper, Lower, Rest, Rest). This provides moderate frequency for muscle groups and is versatile for various experience levels.
- Full Body: Training the entire body in each session, typically 3 days a week with rest days in between. This is fantastic for beginners to build foundational strength and stimulate muscle growth due to high frequency and allows for excellent recovery. It’s also efficient for those with limited gym time.
While body part splits (e.g., Chest Day, Back Day) are common, they often lack the frequency needed for faster progress in muscle gain, especially for natural lifters. For concurrent muscle gain and fat loss, higher frequency (training muscle groups 2-3x/week) is generally more effective.

Tailoring Your Split: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right split isn’t one-size-fits-all. Consider your:
- Training Experience: Beginners often thrive on full-body routines, while intermediates and advanced lifters can handle the higher volume of PPL or Upper/Lower splits.
- Time Commitment: How many days a week can you realistically commit to the gym? A PPL split might require 6 days, an Upper/Lower 4 days, and Full Body 3 days. Consistency is key.
- Recovery Capacity: Are you getting enough sleep, managing stress, and eating adequately? Your recovery dictates how much volume and frequency your body can handle. Overtraining can hinder progress.
It’s crucial to experiment and listen to your body. A split that works for one person may not work for another. Be prepared to adjust your routine based on your progress and how you feel.

Integrating Cardio for Enhanced Fat Loss
While resistance training is crucial for preserving muscle during a caloric deficit, incorporating cardio can significantly accelerate fat loss. There are two main types to consider:
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): Short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. HIIT is very effective for burning calories in a shorter amount of time and can boost your metabolism for hours post-workout. Integrate 2-3 sessions per week on non-lifting days or after your strength training, being mindful of recovery.
- Low-Intensity Steady State (LISS): Longer sessions of moderate-intensity cardio, like walking, jogging, or cycling. LISS is less taxing on the central nervous system, making it easier to recover from and can be done more frequently, even on rest days or as a warm-up/cool-down.
The key is to find a balance that supports your fat loss goals without compromising your strength gains or recovery. Avoid excessive cardio that puts you in too deep a caloric deficit, potentially leading to muscle loss.

The Synergy of Nutrition and Recovery
No workout split, however optimized, can compensate for poor nutrition and inadequate recovery. For simultaneous muscle gain and fat loss:
- Caloric Management: To lose fat, you need a slight caloric deficit (300-500 calories below maintenance). To build muscle, you need adequate calories, making the simultaneous goal a delicate balance. Aim for a modest deficit to facilitate fat loss while maximizing protein intake to support muscle preservation and growth.
- Protein Intake: Consume plenty of protein (1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight) to support muscle repair and growth, especially when in a caloric deficit.
- Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. This is when your body repairs and recovers, and hormone production (like growth hormone and testosterone) is optimized.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water throughout the day. It’s vital for all bodily functions, including metabolism and nutrient transport.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which can hinder fat loss and muscle gain. Incorporate stress-reducing activities into your routine.

Conclusion
Optimizing your workout split is a powerful lever for men aiming for faster muscle gain and fat loss. By understanding the principles of training frequency, volume, and progressive overload, and selecting a split like PPL, Upper/Lower, or Full Body that aligns with your experience and schedule, you can build a highly effective regimen. Remember to integrate smart cardio, prioritize a protein-rich diet, and commit to adequate sleep and recovery. Consistency, patience, and a willingness to adjust are your greatest allies on the journey to a stronger, leaner physique.