Why Durability Matters in Men’s Running Shoes
For dedicated male runners, a pair of running shoes isn’t just footwear; it’s a critical piece of equipment. While comfort, support, and responsiveness are paramount, the longevity of your running shoes directly impacts your training consistency and your wallet. Investing in durable shoes means fewer replacements, more reliable performance over countless miles, and better protection against injuries that can arise from worn-out cushioning or support.
But what exactly makes a running shoe truly durable? It boils down to a combination of material science, construction quality, and thoughtful design. Let’s explore the key features that ensure your running shoes go the distance.
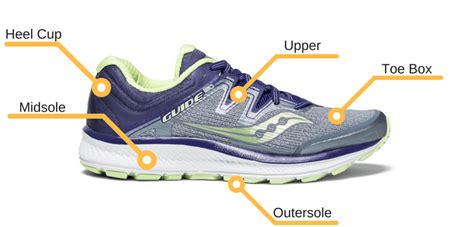
The Foundation: Midsole Durability and Material Science
The midsole is the heart of any running shoe, providing cushioning and energy return. Its ability to maintain these properties over time is crucial for durability. Midsole materials vary widely, and each has a different impact on longevity:
- EVA (Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate): Common and lightweight, but can compress and lose its rebound properties more quickly than other materials. Denser EVA formulations offer better durability.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Known for excellent energy return and superior durability. It resists temperature changes and compression set better than EVA, making shoes with TPU-based midsoles (e.g., Boost, Everun) typically longer-lasting.
- PEBA (Polyether Block Amide): Often found in high-performance racing shoes, PEBA-based foams (e.g., ZoomX, Lightstrike Pro) are incredibly lightweight, responsive, and surprisingly durable for their weight, though they might feel less ‘stable’ over time than denser materials.
- Proprietary Blends: Many brands use unique blends and geometries (like Wave plates, Gel inserts, GuideRails) to enhance both cushioning and durability, distributing impact and resisting breakdown.
Look for midsoles that are resilient to compression and maintain their structure and responsiveness. A thicker midsole doesn’t always equate to more durability; it’s the quality and type of foam that truly matters.

Ground Control: Outsole Toughness and Tread Design
The outsole is your shoe’s first line of defense against abrasion and wear. Its durability is determined by the rubber compound and its design:
- Carbon Rubber: Highly durable, abrasion-resistant rubber typically placed in high-wear areas like the heel and outer edge of the forefoot. It provides excellent longevity but can be slightly heavier and less flexible than blown rubber.
- Blown Rubber: Lighter and softer, offering better cushioning and grip, but less durable than carbon rubber. It’s often used in the forefoot for flexibility and bounce.
- Strategic Placement: Durable shoes often feature carbon rubber in critical areas and sometimes a more flexible, grippy rubber elsewhere. Look for ample rubber coverage, not just thin strips.
- Tread Pattern: Aggressive lug patterns (especially on trail shoes) offer better grip but can wear down faster on pavement. Road shoes need a more uniform, flat pattern for even wear. Deep grooves and strategic flex zones can also enhance durability by preventing cracking.
A full-ground contact outsole, where the entire sole makes contact with the ground, can also contribute to more even wear and prolonged life.
Upper Resilience: Withstanding the Elements and Stress
The upper holds your foot in place and protects it from the elements. A durable upper resists tearing, stretching, and breakdown over time:
- Engineered Mesh: While breathable, some meshes are more robust than others. Look for multi-layered or densely woven engineered mesh with integrated support structures.
- Knit Uppers: Can be comfortable and flexible, but some are prone to snagging or stretching out. Higher-quality knits often incorporate reinforcing fibers or tighter weaves in critical areas.
- Synthetic Overlays and Reinforcements: TPU or synthetic leather overlays around the toe box, midfoot, and heel add significant durability by protecting high-wear zones from scuffs and tears. Welded overlays tend to be lighter and more flexible than stitched ones.
- Ripstop Fabrics: Especially common in trail running shoes, these fabrics are designed to resist tearing and can be found in more rugged road shoes as well.

Structural Integrity: Construction Quality and Attention to Detail
Beyond the materials, how a shoe is put together plays a massive role in its lifespan:
- Stitching and Bonding: Strong, consistent stitching and high-quality bonding agents ensure that different parts of the shoe (upper to midsole, outsole to midsole) stay together without delaminating or falling apart.
- Heel Counter: A firm and well-structured heel counter helps maintain the shoe’s shape and support over time, preventing the heel from collapsing inward or outward.
- Gusseted Tongue: A tongue attached to the sides of the upper helps prevent debris entry and maintains its position, reducing potential rubbing and wear.
- Robust Lacing System: Reinforced eyelets and a secure lacing system prevent premature wear and tear around the lace holes.

The Right Fit: A Durability Factor You Control
While not a shoe feature, the fit of your running shoe directly impacts its longevity. An improperly fitting shoe can lead to premature wear:
- Too Small: Toes rubbing against the front of the shoe can cause tears in the toe box.
- Too Big: Excess movement inside the shoe can create friction, leading to wear spots in the lining and upper.
- Improper Support: If a shoe doesn’t match your foot type (e.g., a neutral shoe for an overpronator), it can lead to uneven wear patterns on the outsole and breakdown of the midsole in specific areas.
Getting professionally fitted can ensure your shoes wear evenly and last longer.
Strategic Reinforcements and Protection
Small but significant details can add to a shoe’s durability:
- Toe Guards: An extra layer of durable material over the toe box protects against scuffs and impacts.
- Rock Plates: While more common in trail shoes, a thin, flexible plate in the forefoot can protect the midsole from sharp objects and extend its life in rugged environments.
- Reinforced Eyelets: Stronger material around the lace holes prevents tearing from consistent lacing and unlacing.
Beyond the Build: Care and Maintenance
Even the most durable shoes benefit from proper care. Cleaning your shoes regularly, allowing them to air dry naturally (never in a dryer), and storing them in a cool, dry place can extend their life. Rotating between two pairs of shoes can also give the midsole foam time to decompress and recover, prolonging the life of both pairs.
Conclusion: An Investment in Your Running Journey
Choosing durable running shoes for men is about making an informed investment. By understanding the importance of midsole resilience, outsole toughness, upper reinforcement, and superior construction quality, you can select footwear that not only supports your performance but also stands the test of time. Prioritizing these features ensures you get the most mileage out of every pair, allowing you to focus on your running goals with confidence and comfort.




