When it comes to power transmission, gears are fundamental components, but their design significantly impacts performance. Two common types, spur gears and helical gears, both transmit motion and power between parallel shafts, yet they differ dramatically in their operational characteristics. While spur gears are widely used for their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, helical gears offer a distinct advantage that makes them superior in many demanding applications.
The Fundamental Difference in Tooth Engagement
To understand the primary advantage of helical gears, it’s essential to first grasp the mechanism of tooth engagement in both types. Spur gears feature straight teeth cut parallel to the gear’s axis. When two spur gears mesh, the contact between teeth occurs simultaneously across the entire width of the tooth face. This sudden, full-face contact is akin to a hammer blow, leading to specific operational characteristics.

Helical Gears: Angled Precision for Smoothness
In contrast, helical gears are designed with teeth cut at an angle, or helix, to the gear’s axis. When these gears mesh, the contact begins gradually at one end of the tooth and progresses smoothly across the tooth face as the gears rotate. This gradual, rolling engagement is the cornerstone of their superior performance. Unlike spur gears, where the load is applied instantaneously across the entire tooth, helical gears distribute the load more progressively.

The Primary Advantage: Quieter and Smoother Operation
The most significant advantage of helical gears over spur gears, particularly in power transmission applications, is their smoother and quieter operation. This benefit directly stems from their gradual tooth engagement. The progressive meshing action minimizes the impact shock that is inherent in spur gears. As a result, helical gears produce substantially less noise and vibration during operation.
In power transmission systems, reduced noise and vibration are critical for several reasons:
- Enhanced Durability: Less shock load on the gear teeth and bearings translates to reduced wear and tear, significantly extending the lifespan of the gearset and associated components.
- Improved Efficiency: Vibration represents wasted energy. By minimizing it, helical gears can operate with higher mechanical efficiency, leading to less power loss and lower operating temperatures.
- Increased Load Capacity: The load is distributed more evenly and continuously over multiple teeth (or across the full width of a single tooth progressively) at any given moment, allowing helical gears to transmit higher loads for a given size compared to spur gears.
- Operator Comfort and Safety: In applications involving human operators, a quieter and smoother running machine reduces fatigue and improves the working environment.

Beyond Quietness: Other Key Benefits and Considerations
While smoother and quieter operation is the primary benefit, helical gears also offer other advantages. Their continuous contact allows for a higher contact ratio, which means more teeth are in contact at any given time, contributing to their ability to handle higher loads and provide more consistent torque transmission. They also experience less backlash compared to spur gears, leading to greater precision in applications requiring accurate positioning.
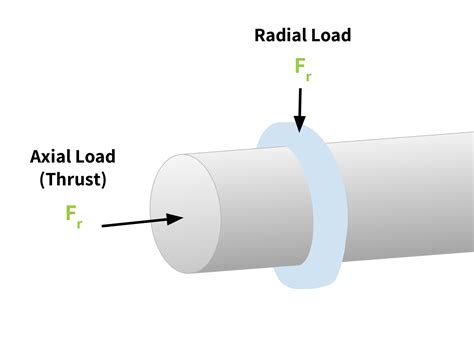
However, it’s important to acknowledge a trade-off: the angled teeth of helical gears generate an axial thrust force along the gear’s axis. This thrust must be accommodated by appropriate thrust bearings in the system, which adds a layer of complexity and cost to the design. Despite this, for many applications where noise, vibration, and high load capacity are critical, the benefits of helical gears far outweigh this design challenge.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary advantage of a helical gear over a spur gear in power transmission applications is its ability to provide significantly smoother and quieter operation, alongside increased load capacity and durability. This is achieved through the gradual engagement of its angled teeth, which eliminates the sudden impact characteristic of spur gears. While helical gears introduce axial thrust, their superior performance in terms of reduced noise, vibration, and enhanced load-carrying capabilities makes them the preferred choice for a wide array of demanding industrial, automotive, and aerospace applications where reliability and operational quality are paramount.





