As men enter their 30s, the physiological landscape of their bodies begins to shift, particularly concerning muscle mass. The rate of muscle protein synthesis (MPS) can decline, and the risk of sarcopenia – age-related muscle loss – increases. For those aiming to build or maintain lean muscle mass, optimizing protein intake becomes not just beneficial, but essential. This article delves into the science-backed recommendations for men over 30 to maximize muscle growth and recovery.
The Crucial Role of Protein in Aging Muscle
Protein is the fundamental building block of muscle tissue. When you exercise, especially through resistance training, you create micro-tears in your muscle fibers. Protein provides the amino acids necessary to repair these tears and rebuild stronger, larger muscles. For men over 30, this process can become less efficient, meaning a slightly higher protein intake may be required to achieve the same anabolic response as younger individuals. It helps counteract the ‘anabolic resistance’ often observed with aging.

General Protein Recommendations: How Much is Enough?
While general guidelines for adults suggest around 0.8 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, men over 30 actively pursuing lean muscle gain will need significantly more. Research indicates that an intake ranging from 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day is optimal for maximizing muscle protein synthesis in resistance-trained individuals. For a man weighing 80 kg (approx. 176 lbs), this translates to roughly 128-176 grams of protein daily.
It’s important to note that these figures are based on lean body mass rather than total body weight for individuals with higher body fat percentages, though using total body weight is a simpler and often effective starting point for most.
Factors Influencing Your Optimal Intake
Activity Level and Training Intensity
The more intensely and frequently you train, the greater your protein requirements will be. High-volume resistance training places a higher demand on muscle repair and recovery, necessitating a robust supply of amino acids.
Calorie Intake and Body Composition Goals
Protein needs can also fluctuate based on whether you are in a calorie surplus (bulking), deficit (cutting), or at maintenance. During a calorie deficit, a higher protein intake (up to 2.4 g/kg body weight or even slightly more) is crucial to preserve lean muscle mass while losing fat. Protein also has a higher thermic effect of food and promotes satiety, aiding in fat loss efforts.

Timing and Distribution: Maximizing MPS
Beyond the total daily amount, how you distribute your protein throughout the day can also impact muscle growth. Aim to consume protein at regular intervals, ideally every 3-4 hours, with each meal containing 20-40 grams of high-quality protein. This strategy helps sustain elevated muscle protein synthesis rates throughout the day.
Consuming protein before and after workouts is particularly beneficial. A pre-workout protein source can provide amino acids during exercise, while post-workout protein helps kickstart recovery and repair. Don’t overlook the importance of a protein source before bed, such as casein protein, which offers a slow and sustained release of amino acids overnight, further supporting muscle repair.

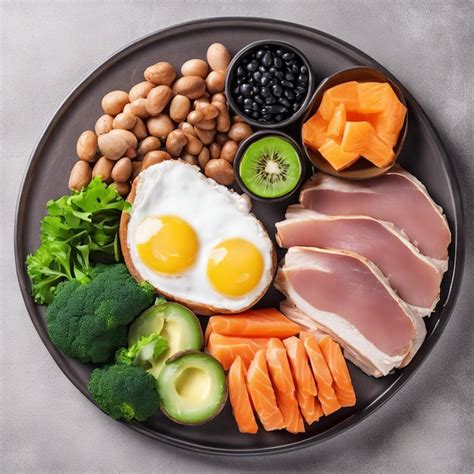
Choosing High-Quality Protein Sources
Not all proteins are created equal. High-quality protein sources contain all nine essential amino acids necessary for muscle protein synthesis. These include:
- Animal Sources: Lean meats (chicken, beef, turkey), fish (salmon, tuna), eggs, dairy (milk, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese).
- Plant Sources: Legumes (beans, lentils), tofu, tempeh, quinoa, nuts, seeds. A combination of plant proteins throughout the day is often needed to ensure a complete amino acid profile.
For convenience or to meet higher targets, protein supplements like whey protein (fast-absorbing), casein protein (slow-absorbing), or plant-based protein powders can be excellent additions to a balanced diet.
Practical Tips for Meeting Your Protein Goals
- Track Your Intake: Use a food tracking app for a few days to get an accurate understanding of your current protein consumption.
- Prioritize Protein: Make protein the focus of every meal and snack.
- Smart Snacking: Opt for protein-rich snacks like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, hard-boiled eggs, or a protein shake.
- Meal Prep: Prepare protein sources in advance (e.g., grilled chicken breasts, boiled eggs) to make healthy eating easier throughout the week.
- Consider Supplements: If struggling to meet targets through whole foods alone, incorporate protein powders strategically.

Conclusion
For men over 30 dedicated to building and maintaining lean muscle mass, an optimal protein intake is a non-negotiable component of their nutritional strategy. Aiming for 1.6 to 2.2 grams of high-quality protein per kilogram of body weight daily, distributed strategically across meals, and paired with consistent resistance training, provides the best foundation for muscle growth and combating age-related muscle decline. By prioritizing protein, you can effectively support your body’s ability to repair, recover, and build the muscle you desire well into your prime years.




